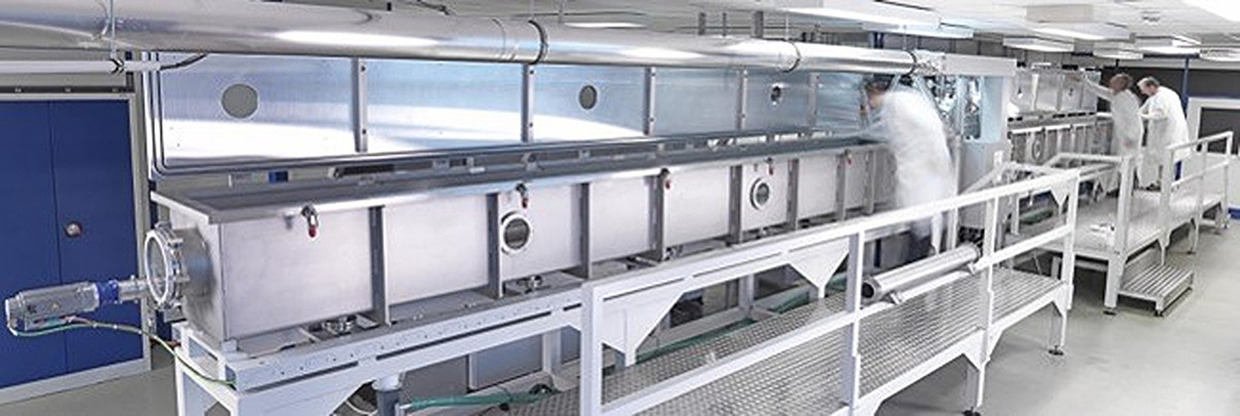
KC4: Bridging Research and Application in Coated Conductors

Advancements in High-Temperature Superconductors for Applied Technologies
In recent years, high-temperature superconductors (HTS) have been intensively developed for various applications such as high-field magnets, fusion magnets, and current limiters. REBCO HTS tapes used in these applications are hybrid materials consisting of thin, layered superconducting tapes within a multilayered coated conductor (CC) structure made of metals such as silver, copper, or stainless steel.
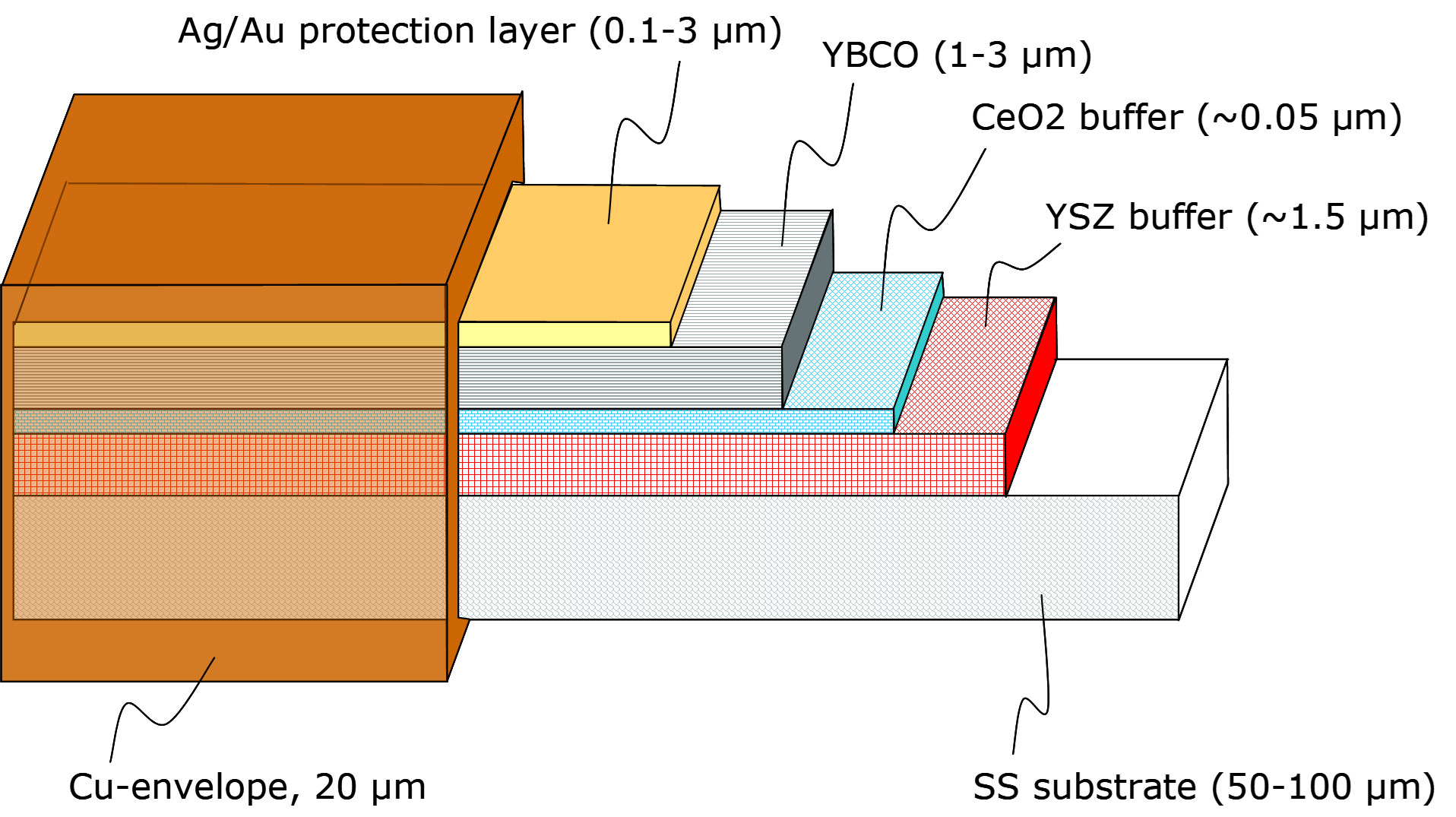
The performance of such superconducting tapes is characterized by several parameters, including critical temperature, critical current (Ic) under different technological conditions (e.g., high magnetic fields and low temperatures), interfacial resistance, and electro-mechanical properties.
KC4 (KIT-CERN Collaboration on Coated Conductors) at ITEP is a unique, open-access HTS coated conductor synthesis laboratory that aims to bridge the gap between small-scale laboratory research and the production of longer tape lengths suitable for a range of applications. It is KIT and CERN joint R&D Project 2022-2026 based on established Bruker CC-technology for long CC and wide tapes.
Running research topics
The Role of KC4 in Scalable HTS Tape Production
To produce high-quality coated conductors with specified properties, numerous parameters must be carefully controlled.

Interfacial Resistance: A Key Factor in HTS Tape Performance
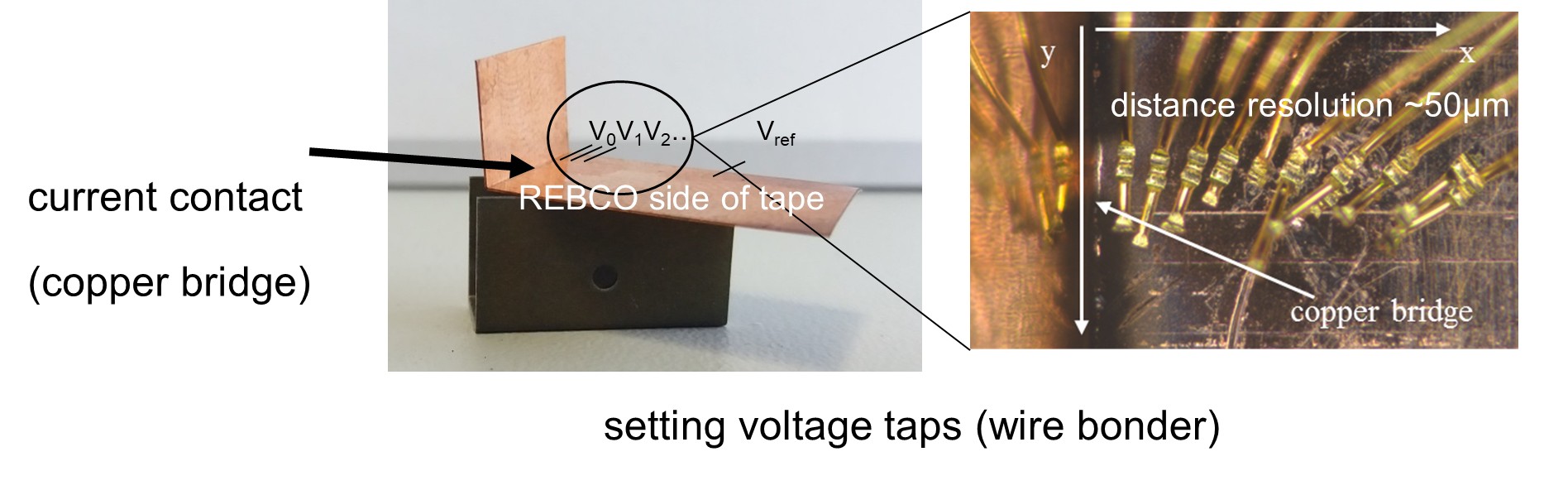
One important characteristic of an HTS tape is its interfacial resistance between the superconducting layer and the surrounding layers. This resistance strongly influences the current transfer length (CTL) and the normal zone propagation (NZP) velocity. However, interfacial resistance often varies by orders of magnitude in commercially available HTS tapes, which poses a significant challenge. These variations may result from differences in the deposition methods of the first metallic layer, handling of the tape prior to silver deposition, or the quality of the silver layer itself. To better understand these systematic influences, KC4-produced tapes incorporate variations in silver deposition parameters and different silver alloys.
Electromechanical Performance and Its Impact on HTS Usability
Another crucial parameter is the electromechanical performance of HTS tapes. It is well known that this performance varies significantly between manufacturers and even between different batches from the same manufacturer. This variability is particularly problematic for high magnetic field applications, where differences in delamination strength or the dependence of Ic on tensile and compressive loads can substantially limit tape usability. Therefore, research at KC4 focuses on improving the understanding of the underlying factors that influence electromechanical performance — especially delamination strength — to enhance the suitability of these tapes for high-field applications.
Artificial Pinning Experiments
Special applications—such as those involving low temperatures and high magnetic fields—require tailored tuning of REBCO material to effectively "pin" magnetic field vortices. This pinning prevents their movement and "freezes" the magnetic field within the superconducting matrix. Such tuning can be achieved by introducing artificial pinning centers into the REBCO material. While many laboratory-scale experiments have already been conducted and published, it is crucial to transfer this know-how to the production of practical coated conductors (CC). The KC4 line presents a valuable opportunity for this purpose.


